Webhooks
Webhooks allow Admiral to send real-time JSON payloads to your endpoints when specific events occur.
What Are Webhooks?
Instead of polling the Admiral API for changes, webhooks push notifications to your application immediately when events happen.
Benefits:
- Real-time notifications
- Reduced API calls
- Event-driven architecture
- Integration with external systems
Creating a Webhook
- Go to Settings > Webhooks
- Click New Webhook
- Configure the webhook settings
- Click Create
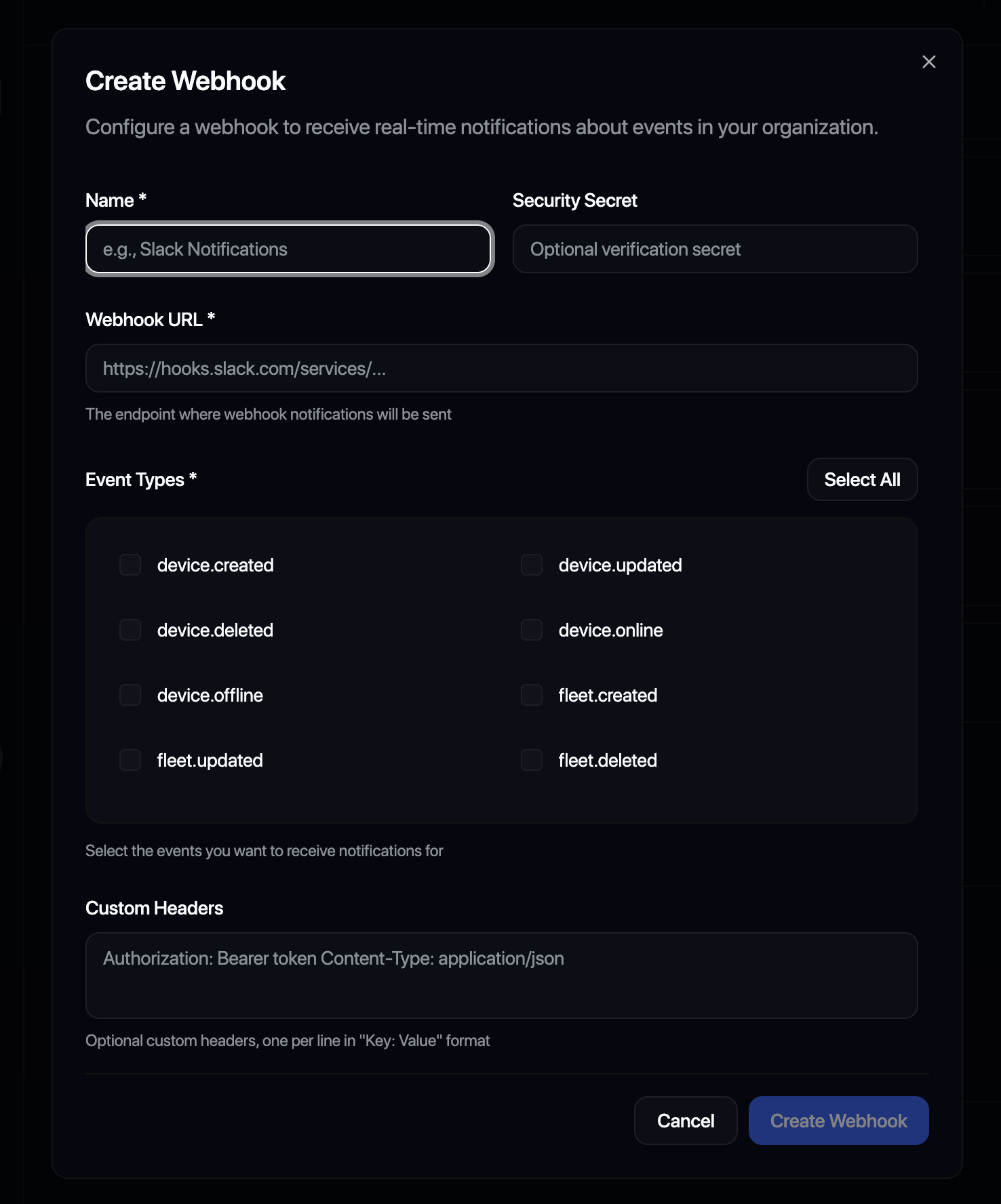
Webhook Configuration
Endpoint URL
The HTTPS URL where Admiral will send event payloads:
https://your-app.example.com/webhooks/admiral
Requirements:
- Must use HTTPS (HTTP not supported for security)
- Must return 2xx status code within 10 seconds
- Must be publicly accessible (or use a webhook relay service)
Events
Select which events trigger the webhook:
Fleet Events:
fleet.node.added- A device was added to a fleetfleet.node.removed- A device was removed from a fleetfleet.auto_induction- A device automatically joined via provisioning profile
Node (Device) Events:
node.online- Device connected to control planenode.offline- Device disconnectednode.started- Admiral agent startednode.shutdown- Device is shutting downnode.restarted- Device rebooted
Workload Events:
workload.started- Container workload startedworkload.stopped- Container workload stoppedworkload.restarted- Container workload restartedworkload.crashed- Container workload exited unexpectedly
Custom Headers
Add custom HTTP headers to webhook requests.
Common use cases:
Authentication:
Key: Authorization
Value: Bearer your-secret-token
API Keys:
Key: X-API-Key
Value: your-api-key
Custom Routing:
Key: X-Webhook-Source
Value: admiral-production
Secret
When you create a webhook, Admiral automatically generates a unique Signing Secret. This secret is used to sign payloads so you can verify they originated from Admiral.
Webhook Headers
Admiral sends the following headers with every request:
User-Agent:Admiral-Webhook-Service/1.0Content-Type:application/jsonX-Admiral-Event: The event type (e.g.,node.offline)X-Admiral-Delivery: A unique UUID for this specific delivery attemptX-Admiral-Signature: The HMAC SHA256 signature of the payload (if a secret exists)
Webhook Payloads
Payload Structure
All webhooks follow this structure:
{
"type": "node.offline",
"timestamp": "2024-01-15T10:23:45Z",
"organisation_id": "org_abc123",
"data": {
// Event-specific data
}
}
Example Payloads
Node Offline
{
"type": "node.offline",
"timestamp": "2024-01-15T10:23:45Z",
"organisation_id": "org_abc123",
"data": {
"device_id": "dev_xyz789",
"device_name": "NYC-Store-Display-01",
"fleet_id": "fleet_456",
"fleet_name": "Retail-NYC",
"last_seen": "2024-01-15T10:20:12Z"
}
}
Workload Crashed
{
"type": "workload.crashed",
"timestamp": "2024-01-15T11:45:30Z",
"organisation_id": "org_abc123",
"data": {
"device_id": "dev_xyz789",
"container_id": "cont_999",
"image": "my-app:latest",
"exit_code": 137,
"reason": "OOMKilled"
}
}
Fleet Node Added
{
"type": "fleet.node.added",
"timestamp": "2024-01-15T09:15:22Z",
"organisation_id": "org_abc123",
"data": {
"device_id": "dev_new001",
"device_name": "LA-Warehouse-Scanner-05",
"fleet_id": "fleet_789",
"fleet_name": "Warehouse-LA"
}
}
Verifying Webhooks
Signature Verification
Admiral signs the payload body using HMAC SHA256 with your webhook's secret. The signature is sent in the X-Admiral-Signature header.
Format: sha256=<hex_signature>
Here is a Python example to verify the signature:
import hmac
import hashlib
def verify_webhook(payload_bytes, signature_header, secret):
# Remove "sha256=" prefix
if signature_header.startswith("sha256="):
signature = signature_header[7:]
else:
return False
# Calculate expected signature
expected_signature = hmac.new(
secret.encode('utf-8'),
payload_bytes,
hashlib.sha256
).hexdigest()
# Constant time comparison to prevent timing attacks
return hmac.compare_digest(expected_signature, signature)
# In your webhook handler
payload = request.body # Raw bytes
signature = request.headers.get('X-Admiral-Signature')
secret = 'your-webhook-secret'
if verify_webhook(payload, signature, secret):
# Process webhook
process_event(payload)
else:
# Reject invalid webhook
return 401
Integration Examples
Slack Notifications
import requests
def handle_node_offline(webhook_data):
data = webhook_data['data']
device_name = data.get('device_name', 'Unknown Device')
fleet_name = data.get('fleet_name', 'Unknown Fleet')
slack_message = {
"text": f"🔴 Device Offline Alert",
"blocks": [
{
"type": "section",
"text": {
"type": "mrkdwn",
"text": f"*Device:* {device_name}\n*Fleet:* {fleet_name}"
}
}
]
}
requests.post(
"https://hooks.slack.com/services/YOUR/WEBHOOK/URL",
json=slack_message
)
Database Logging
import json
def log_webhook_to_database(webhook_data):
# webhook_data matches the SystemEvent structure
db.execute("""
INSERT INTO admiral_events (event_type, timestamp, organisation_id, data)
VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?)
""", (
webhook_data['type'],
webhook_data['timestamp'],
webhook_data['organisation_id'],
json.dumps(webhook_data['data'])
))
Webhook Management
Disabling Webhooks
You can temporarily disable a webhook without deleting it. Disabled webhooks will not receive any events until re-enabled.